PRODUCT CATEGORY
PRODUCT CATEGORY
CONTACT US
Phone
Email
Address
Building 109, 1 Cuizhu Street, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
TTF-1/Napsin A detection reagent (Immunohistochemical)
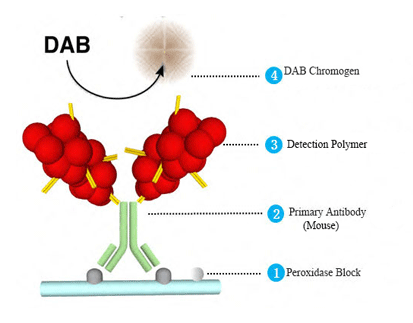
TTF-1/Napsin A detection reagent (Immunohistochemical) is mainly used to qualitatively identify TTF-1 and Napsin A proteins. Using immunohistochemical dual staining detection and multiple antibody combination technology, there are detected two antigen targets at the same time on the same sample tissue section by one staining process.
Specification
|
Model Number |
Specification |
|
SD8101 |
1mL/pcs; 3mL/pcs; 7/pcs |
This antibody is used with Immune Chromogenic Reagent (Dual Staining I) (SD8001)
Clone: Mym1-TTF1 + BP6083
More Info
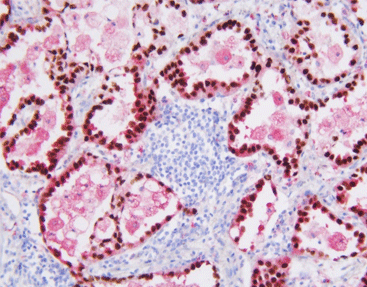
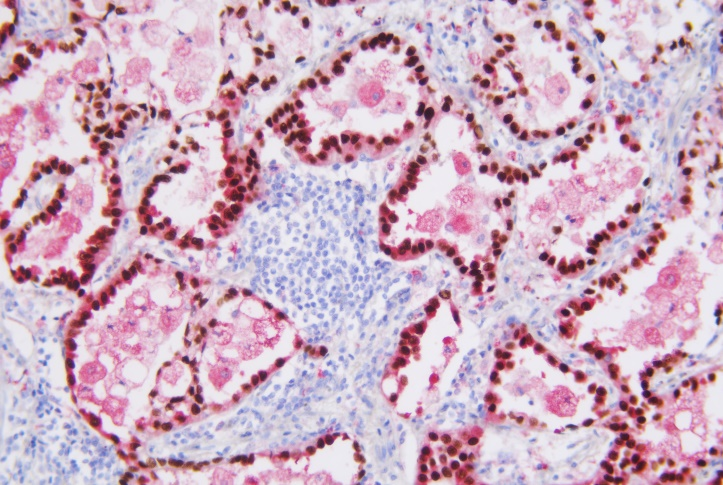
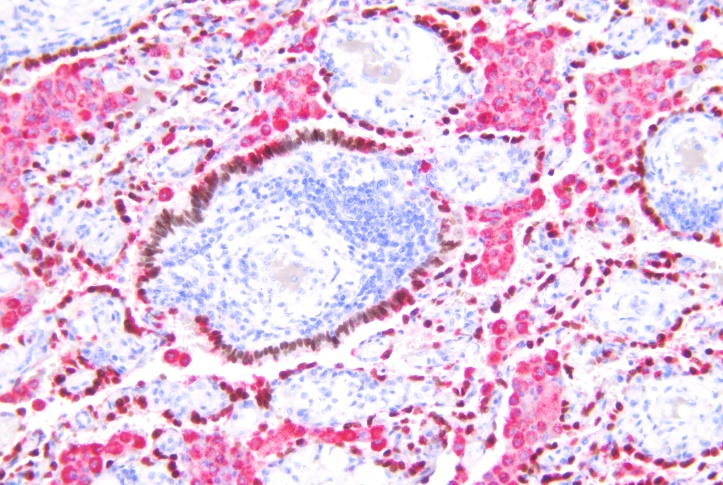
TTF-1 is expressed in the nucleus of thyroid follicular epithelium and alveolar epithelial cells. It is the primary marker for the differential diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma. TTF-1 is expressed in more than 70% of non-mucinous adenocarcinoma subtypes, small cell lung cancer, a small portion of undifferentiated large cell lung cancer and atypical carcinoids, a small number of typical carcinoids. In addition, a small number of lung squamous cell carcinomas show TTF-1 positive expression.
Napsin A is expressed in normal alveolar type II epithelial cells and proximal and distal renal tubules. Napsin A shows positive in 80%~90% of lung adenocarcinomas. But Napsin A shows negative expression in almost all lung squamous cell carcinomas. The sensitivity and specificity of Napsin A are better than TTF-1. TTF-1/Napsin A combined primary antibody show higher sensitivity.
In non-small cell lung cancer, positive expression of TTF-1 and negative expression of NapsinA can occur in some large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma similar to adenocarcinoma. TTF-1/Napsin A combined primary antibody can effectively identify these tumor diseases.
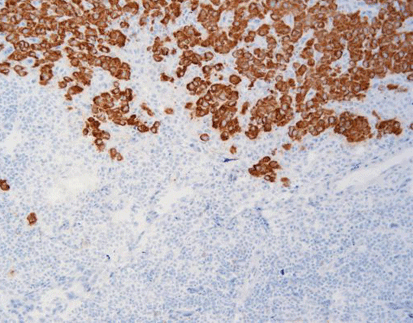
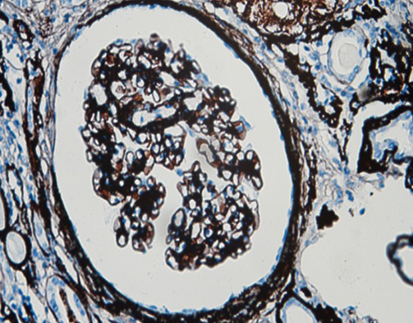
TTF-1 lung adenocarcinoma-nucleus (brown)
NapsinA-lung adenocarcinoma-cytoplasm (brown)