Molecular Pathology(FISH Probe)
Molecular pathology can be broadly defined as the testing of nucleic acids within a clinical context. The applications of molecular diagnostics span a range of human disorders, including hereditary, neoplastic, and infectious diseases. This type of testing can also be utilized to assess malignancies for staging or diagnostic uses.
In molecular pathology, pathologist will analyze DNA and other genetic material for the purpose of diagnosing or monitoring disease. Through molecular and genetic approaches, molecular pathology techniques are used across a variety of specialties to diagnose and assess risk for a multitude of diseases. Personalized medicine, utilizing strategies that include molecular pathology techniques, can use specific information related to the patient’s tumor to help diagnose, plan treatment, assess the effectiveness of a treatment, or develop a prognosis. Targeted therapies can even be used to treat specific classes of cancer cells, or identify tumor markers that can help diagnose cancer.
FISH techology applications in molecular pathology
- Copy number (Gene-specific
probes also called LSI probes) :
– Amplifications (ex.: HER2 in breast
and gastic cancer)
– Deletions (ex.: P16 deletion in
ALL)
- Rearangements (Break Apart, Dual
Fusion):
– Translocations (ex.: t(X;18) in
Synovial Sarcoma)
– Inversions (ex.: ALK rearrangement
in lung cancer)
- Chromosome EnumerationProbes (CEP)
- Telomeres
FISH probes
Ewing’s Sarcoma is a small, round, blue cell tumour belonging to the family of primitive neuroendocrine tumours. In over 85% of cases a translocation between chromosome 22 and 11 is seen (EWSR1 gene fuses with FLI1 gene). Other translocations also occur: t(7;22) and t(21;22). A break-apart probe indentifies all cases with break in the EWSR1 gene region. This covers all translocations in Ewing’s Sarcoma helping in differential diagnosis between ES and rhabdomyosarcoma.

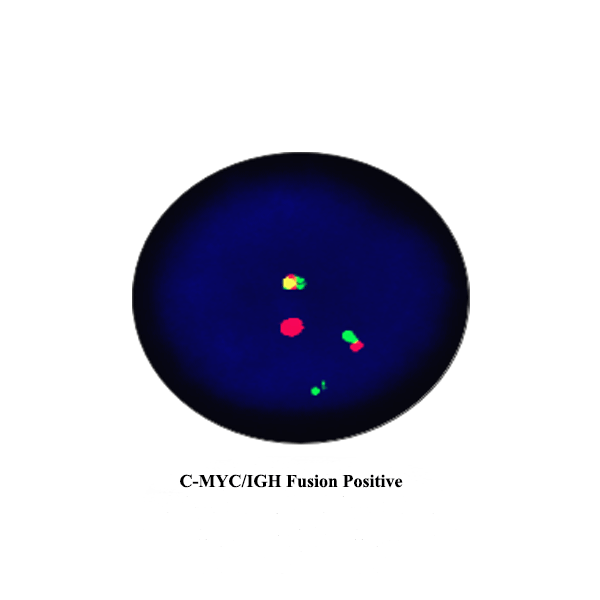
c-MYC is regularoty gene which encodes for the transcription factor, which is multifunctional and regulates cell cycle and proliferation. A common translocation in the area of c-MYC gene is critical in the development of most cases of Burkitt Lymphoma. Amplification of c-MYC gene can be found in cervical, colon, breast, lung and stomach cancers. MYC is perceived as a promising target to anti-cancer therapies.
https://www.celnovte.com/c-myc-igh-fusion-gene-detection-kit/
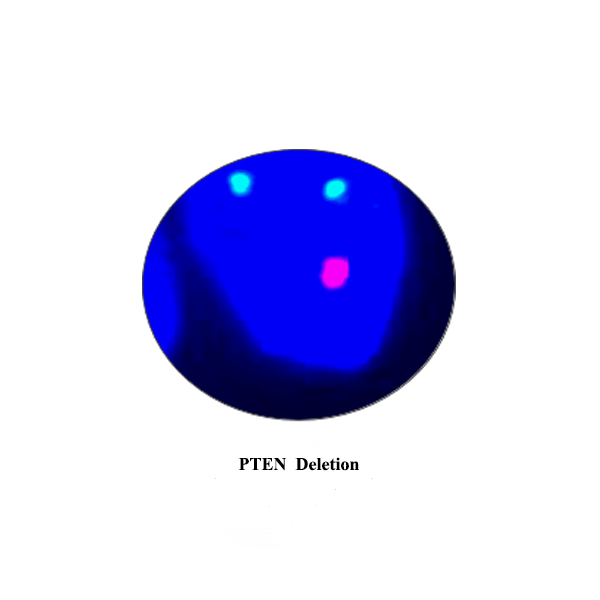
PTEN is tumour suppressor gene. Its allelic loss results in malignant progression of various types of cancer, prostate being the frequent one. Approximately 60% of prostate cancers harbour PTEN allelic loss.
PTEN in prostate cancer https://www.celnovte.com/pten-gene-detection-kit/
More deteails : https://www.celnovte.com/product-center/?cat=10
Contact us info@celnovte-bio-tech.com