-
Home
-
Product
-
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
-
INSTRUMENT
-
MOLECULAR
-
HISTOLOGY
-
CYTOLOGY
-
DIGITAL PATHOLOGY
-
-
Solution
-
Support
-
About
-
Contact

Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Techniques in Pathology
Advantages of FISH
- No need of cell culture.
- FISH can be done on paraffin cell blockmaterial.
- Archival tissue can be used for FISH.
- Morphology of the cell can be seenalong with cytogenetic abnormalities.
- High resolution.
- The slide can be stored for long time.
- Fluorescent tags are safe and simple.
Limitations of FISH: FISH has following limitations:
- The FISH technique can be used only in thecase of known chromosomal abnormalities aswe use only the specific probes.
- It is not suitable for a screening test as onlyknown chromosomal probes are used,whereas in cell culture or conventional technique, we may get a wide range of chromosomal abnormalities.
- FISH does not give any allele-specificinformation.
Applications of FISH:
- Gain and loss of chromosome: FISH is helpful to detect total gain or loss of chromosomesuch as trisomy 12 in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia which can be detected by FISH in cytology or histology sample.
- Chromosomal rearrangements: FISH is helpful to identify typical chromosomaltranslocation such as t (11; 22) (q24; q12) inEwing’s/primitive neuroectodermal tumor [4].
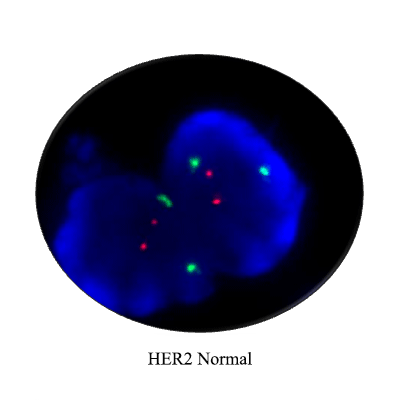
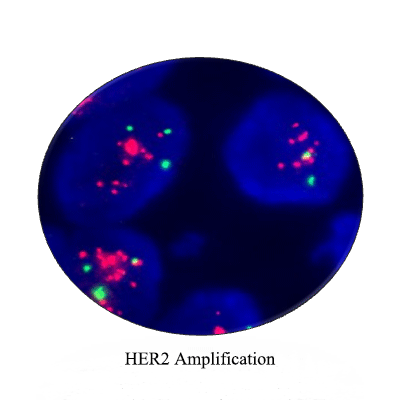
- Gene amplification: Gene amplification suchas HER-2 in breast carcinoma can be detectedby FISH.
- Gene deletion: Gene deletion such as 9p21deletion in urothelial cell carcinoma can be detected by FISH.
- Disease monitoring: To assess the progressionor regression of disease and also to identify the minimal residual disease.
More details about FISH probes https://www.celnovte.com/product-center/?cat=10
Contact us info@celnovte-bio-tech.com
Reference
Pranab Dey, Basic and Advanced Laboratory Techniques in Histopathology and Cytology (2018): 213-214