Unraveling Thyroglobulin Antibody: A Clinical Guide
 2024-05-28
2024-05-28
By admin
Thyroglobulin antibody serves as a crucial marker for autoimmune thyroid disease, the primary cause of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism in the United States. Its presence, detected in about 10% of the general population, signifies underlying conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Understanding thyroglobulin antibody is paramount for comprehending thyroid health intricacies and navigating through potential diagnoses. This guide aims to shed light on the significance of thyroglobulin antibody in clinical settings, offering insights into its implications on thyroid function and overall well-being.
Understanding Thyroglobulin Antibody
Definition and Function
Thyroglobulin is a crucial protein produced by both normal and cancerous thyroid cells. It plays a vital role in the body, particularly in the context of thyroid health. When individuals undergo treatment for thyroid cancer, which often involves total thyroidectomy and subsequent therapies, monitoring the serum thyroglobulin level becomes essential. This monitoring helps in assessing the presence of any residual normal thyroid cells or cancerous cells. Notably, elevated levels of thyroglobulin can indicate the presence of thyroid cancer cells, making it a valuable marker for disease progression.
Thyroglobulin antibodies, on the other hand, are directed against the thyroglobulin molecule itself. These antibodies are found in approximately 10% of the general population and can be raised in individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Studies have shown that positive thyroglobulin antibodies are associated with an increased risk of thyroid cancer. Therefore, high levels of these antibodies can serve as an indicator for potential malignancy and aid in the diagnostic process.
Associated Conditions
Hashimoto’s Disease
Hashimoto’s disease is a common autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland. Individuals with Hashimoto’s disease often have elevated levels of thyroglobulin antibody, indicating an immune response against their own thyroid tissue. This condition can lead to hypothyroidism over time if left untreated.
Other Thyroid Disorders
Apart from Hashimoto’s disease, elevated levels of thyroglobulin antibody may also be present in other thyroid disorders such as Graves’ disease or postpartum thyroiditis. Monitoring these antibody levels alongside other diagnostic tests is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management of various thyroid conditions.
Clinical Significance
Impact on Thyroid Health
Hypothyroidism
Elevated levels of thyroglobulin antibody can have a significant impact on thyroid health, particularly leading to hypothyroidism. When the body’s immune system produces antibodies against thyroglobulin, it can interfere with the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. This disruption often results in an underactive thyroid, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold. Monitoring thyroglobulin antibody levels is crucial in assessing the risk of developing hypothyroidism and initiating appropriate management strategies.
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis, characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland, is another condition closely linked to thyroglobulin antibodies. The presence of these antibodies indicates an autoimmune response targeting the thyroid tissue. In cases of chronic thyroiditis, such as Hashimoto’s disease, persistent elevation of thyroglobulin antibody levels can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the destruction of thyroid cells. This process ultimately leads to thyroid dysfunction and may manifest as symptoms associated with both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Cancer Management
Role in monitoring
In the context of thyroid cancer management, monitoring thyroglobulin antibody levels plays a vital role in assessing disease progression and recurrence. Patients who have undergone treatment for thyroid cancer are regularly monitored for any signs of residual or recurrent cancer cells. Elevated levels of thyroglobulin antibodies post-treatment can indicate persistent disease activity or metastasis. By tracking these antibody levels over time, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding further interventions or adjustments to the existing treatment plan.
Post-operative follow-up
Following surgical intervention for thyroid cancer, post-operative follow-up includes evaluating thyroglobulin antibody levels as part of routine surveillance. Detecting any increase in these antibodies post-surgery may signal residual cancerous tissue or recurrence. Therefore, regular monitoring through specific blood tests helps in early detection and timely management of any potential complications. Close collaboration between endocrinologists and oncologists is essential during this phase to ensure comprehensive care for patients undergoing post-operative follow-up.
Other Health Implications
Cholesterol Levels
Research has shown a correlation between elevated thyroglobulin antibody levels and increased cholesterol levels in individuals with autoimmune thyroid conditions. High cholesterol poses additional risks to cardiovascular health and may exacerbate existing metabolic imbalances associated with thyroid dysfunction. Managing lipid profiles through dietary modifications and medication becomes crucial in individuals with elevated thyroglobulin antibodies, aiming to mitigate cardiovascular risks effectively.
Selenium Supplementation
Selenium supplementation has emerged as a potential adjunct therapy for individuals with low selenium concentrations and autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s disease associated with elevated thyroglobulin antibody levels. Selenium plays a crucial role in antioxidant defense mechanisms within the body and may help reduce inflammatory processes targeting the thyroid gland. Integrating selenium supplementation under medical supervision offers a promising avenue for managing autoimmune thyroid disorders effectively.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnostic Testing
Thyroglobulin antibody testing
Thyroglobulin antibody testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing autoimmune thyroid conditions and monitoring thyroid health. A positive result on this test indicates the presence of antibodies targeting thyroglobulin, a key protein in thyroid function. Healthcare providers use this information to assess the immune response against the thyroid gland, aiding in the early detection of potential thyroid disorders.
Interpreting test results
Interpreting thyroglobulin antibody test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the reference ranges and clinical implications. Elevated levels of thyroglobulin antibodies may suggest underlying autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s disease or Graves’ disease. Conversely, normal levels do not entirely rule out thyroid disorders, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach to diagnosis and management based on individual patient profiles.
Treatment Options
Managing Hashimoto’s disease
The management of Hashimoto’s disease involves addressing the underlying autoimmune response and restoring thyroid function. Healthcare providers may recommend hormone replacement therapy to regulate thyroid hormone levels and alleviate symptoms of hypothyroidism. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and stress management techniques play a vital role in supporting overall well-being for individuals with Hashimoto’s disease.
Addressing thyroid cancer
In cases where thyroglobulin antibodies are associated with thyroid cancer, treatment strategies focus on cancer management and surveillance. Surgical interventions, radioactive iodine therapy, or targeted therapies may be employed based on the extent and aggressiveness of the cancer. Regular monitoring of thyroglobulin antibody levels post-treatment helps healthcare providers track disease progression and tailor interventions accordingly.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular testing
Regular monitoring of thyroglobulin antibody levels is essential for tracking changes in immune response patterns and evaluating treatment efficacy. Patients with autoimmune thyroid conditions or a history of thyroid cancer undergo periodic blood tests to assess thyroglobulin antibody levels. These tests provide valuable insights into disease activity, guiding adjustments in treatment plans as needed.
Long-term management
Long-term management of thyroglobulin antibodies involves collaborative care between endocrinologists, oncologists, and primary care providers. Establishing individual care plans that address both the immune system’s reaction and general thyroid function is key to improving patient results. Continuous tracking through regular follow-ups enables prompt action in case of disease return or development.
In summary, knowing the role of thyroglobulin antibodies in thyroid health is essential for accurate detection and effective treatment of linked diseases. Monitoring thyroglobulin antibody levels offers important insights into autoimmune reactions and possible disease development.
Recognizing the importance of these antibodies may aid healthcare personnel in establishing personalised treatment regimens and improved patient outcomes over time. Moving ahead, continuous investigation and advances in thyroglobulin antibody testing will boost detection accuracy and better treatment techniques for persons with thyroid diseases.
Staying informed about the latest breakthroughs in this area is important for better patient care and well-being.
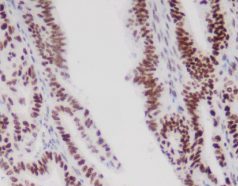
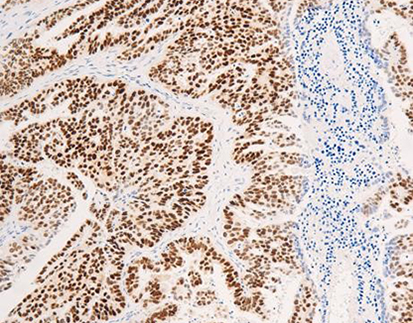
Thyroglobulin antibody is one of the immunohistochemical reagents offered by Celnovte, a high-tech company that specialises in precision diagnostic tools and reagents for malignancies. Application of this antibody is found in many fields, chief among them being target identification and drug development. Celnovte offers a specialist antibody development team that enables the customisation of murine monoclonal antibodies and human monoclonal antibodies, guaranteeing high sensitivity and excellent specificity for successful research.
Celnovte offers a number of immunohistochemistry tools, including the thyroglobulin antibody. This antibody is used for target identification and drug creation in different studies.
Celnovte has a professional antibody development team that supports customized development services for both murine monoclonal antibodies and human monoclonal antibodies. The thyroglobulin antibody is meant to give high sensitivity and good specificity, making it a great tool for creative study in the area of tumor pathology detection. Celnovte’s commitment to quality and innovation ensures that their thyroglobulin antibody, along with their other goods, meets the greatest standards in the business. Besides antibody, Celnovte also provide high-quality instrument, including IHC stainers, cytology stainers, and others
In summary, understanding the role of thyroglobulin antibodies in thyroid health is important for correct identification and proper treatment of related diseases. One may learn vital information about inflammatory responses and potential illness development by tracking thyroglobulin antibodies levels. Realising the function of these antibodies might help medical professionals create specialised treatment plans and eventually provide improved patient outcomes. More studies and developments in thyroglobulin antibody testing will soon improve treatment regimes for thyroid patients and increase spotting accuracy.