Unlocking Cervical Precancer Detection: Understanding p16/Ki-67 Biomarkers

By admin
P16 and Ki-67 play roles in identifying cervical precancers by signaling cell cycle control and growth activity within cells of interest. P16 expression is triggered by oncogene activation like HPV infection, while Ki-67 indicates proliferation. The combination of these markers offers information about how cervical cells function biologically and aids in making more precise evaluations, in medical settings.
Key Concepts of p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining
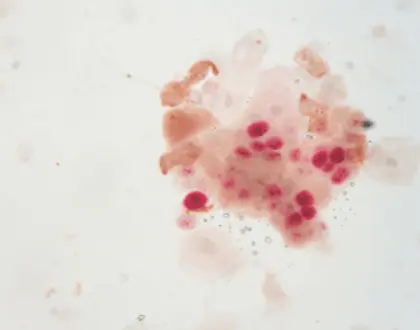
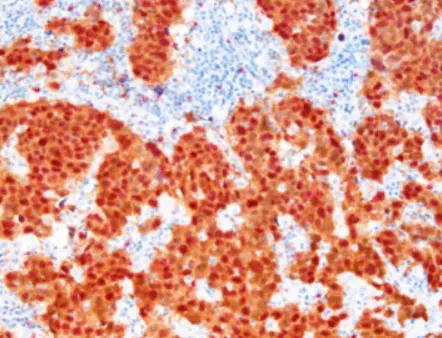
The method of staining for p16 and Ki‐67 is a valuable technique to detect both of these markers simultaneously in a single tissue or cytology sample efficiently. This strategy improves accuracy for precancerous lesions by leveraging their distinct expression patterns. The co‐localization of p16 and Ki‐67 in tissues is associated with high‐grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) or cervical cancer presence. Therefore using p16/Ki‐67 staining is crucial for distinguishing between benign and malignant changes, in cervical epithelia.
Why Are They Critical for Cervical Precancer Detection?
Identifying precancers using p16/Ki-67 markers greatly enhances diagnostic accuracy and precision—a crucial factor in early detection and treatment planning that can impact disease progression significantly. It is imperative to pinpoint conditions accurately to lower cervical cancer risks and improve patient results. Incorporating p16/Ki-67 biomarkers into screenings offers clinicians a valuable tool, for their practice.
How Does p16-Ki-67 Dual Stain Cytology Work?
The methodology of p16 and Ki-67 dual stain cytology revolves around immunohistochemistry techniques that allow for the visualization of these proteins in tissue samples. In practice, samples are treated with specific antibodies that selectively bind to p16 and Ki-67, resulting in different staining patterns observable under a microscope. This visual representation assists pathologists in evaluating cell changes more accurately and identifying significant precancerous alterations.
Methods for Testing Using p16-Ki-67
Several testing methods utilize the p16/Ki-67 dual staining technique. Common approaches include employing cytological specimens obtained from Pap smears, where abnormal cells can be directly evaluated for p16 and Ki-67 expression. Tissue biopsy samples can also be subjected to dual staining, providing additional context for identified lesions. Each method enhances diagnostic confidence and the ability to diagnose cervical precancer effectively.
Sensitivity and Specificity of p16-Ki-67 Dual Staining
The dual staining system is recognized for its elevated sensitivity and specificity compared to traditional cytology methods alone. Its ability to identify high-risk lesions while minimizing false negatives is a substantial advantage. Studies show that this approach can significantly reduce the incidence of missed diagnoses, thereby advancing early detection and treatment protocols. Therefore, the p16/Ki-67 dual staining method enhances the overall efficacy of cervical cancer screening programs.
How Effective is Dual Stain Cytology in Clinical Settings?
The effectiveness of p16/Ki-67 dual stain cytology is well-documented in diverse clinical studies. It is particularly useful in screening programs, as it streamlines the identification of high-grade lesions and reduces unnecessary follow-ups. The integration of these biomarkers into existing frameworks relies on solid performance metrics, which demonstrate improved diagnostic capabilities.
Performance Metrics in Diverse Populations
Performance metrics indicate that dual staining shows consistent results across varied populations, enhancing its credibility as a diagnostic tool. These studies reveal a correlation between dual staining results and the histological findings of tissue samples, reinforcing confidence in the biomarkers’ roles in cervical precancer detection. The adaptability of this testing method in diverse demographic groups further highlights its relevance in global health contexts.
Application in HPV Negative Patients
The application of p16/Ki-67 dual staining extends to HPV-negative patients, which presents unique challenges in cervical cancer screening. In this particular demographic, determining risk levels for cervical precancer can be complex. However, utilizing p16/Ki-67 offers a pathway to accurately assess cytological changes that may not directly correlate with HPV status alone. As such, this dual staining framework serves as a valuable addition to the diagnostic toolkit in gynecologic pathologies.
Solutions
For labs looking for ways to detect early signs of cervical cancer accurately and efficiently p16/Ki-67 dual staining can be a valuable method to consider. Implementing techniques in immunohistochemistry can lead to better results, for patients and smoother operational processes. For more information, you can visit Celnovte Solutions. Moreover, for those interested in procuring p16/Ki-67 detection reagents, the P16/Ki-67 Dual Staining Detection Kit is a recommended choice.
In summary, the progress in detecting p16 and Ki‐67 biomarkers offers a chance to improve cervical cancer screening efforts, resulting in better strategies, for managing patients. Healthcare providers who grasp and apply these biomarkers can greatly enhance precision and patient results.
What Are Emerging Biomarkers Complementary to p16/Ki-67?
New Molecular Targets for Early Detection
Recent research indicates that several new molecular targets have emerged as significant complements to p16/Ki-67 in cervical precancer detection. These biomarkers include proteins associated with cell cycle regulation and tumorigenesis, thus offering additional avenues for accurate early detection. Consider this example, biomarkers such as papillomavirus (HPV) E6 and E7 oncoproteins offer valuable insights into viral oncogenic properties and greatly improve diagnostic capabilities in this area of study. Pairing these molecular markers, with p16/Ki-67 allows healthcare providers to gain a broader understanding of cervical tissue abnormalities and facilitates prompt intervention when necessary.
Advancements in Precision Medicine
The way doctors diagnose and treat cancer is changing because of advancements in precision medicine technology. They can improve how well their treatment plans work by customizing them to fit each person’s biomarker information. Bringing in biomarkers like p16/Ki-67 alongside other tests gives a deeper insight into how the disease is developing and makes personalized treatment choices easier. This focused method helps reduce treatments and make sure patients at high risk get proper care and monitoring.
Solutions for Clinics: Enhancing Cervical Precancer Detection
To enhance cervical precancer detection, healthcare systems must adopt strategic implementation protocols for p16/Ki-67 alongside emerging biomarkers. This may involve training healthcare professionals to accurately interpret dual staining results and integrate new diagnostic workflows into clinical practice. Moreover, timely data sharing and communication between laboratories and clinicians facilitate crucial decision-making processes, ultimately improving patient care. Utilizing resources and solutions like those offered by Celnovte can assist clinics in developing these capabilities, ensuring they stay at the forefront of cervical cancer screening advancements.
Engaging Stakeholders and Building Awareness
Effective stakeholder engagement is critical for the successful implementation of enhanced cervical cancer detection methods. Educational initiatives aimed at both healthcare staff and patients can promote awareness of the importance of utilizing biomarkers like p16/Ki-67. These programs should highlight the benefits of early detection protocols and how they can lead to improved clinical outcomes. Building consensus among healthcare providers, policymakers, and patient advocates can foster wider adoption of these innovative diagnostics, ultimately transforming cervical cancer management.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Implementing p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining
Evaluate costs and benefits to assess whether incorporating p16/Ki-67 dual staining in clinical practice is feasible or not important initial expenses in training technology and acquiring reagents should be balanced with potential long-term benefits such as decreased cervical cancer cases and lower mortality rates for clinics integrating cutting edge biomarkers could enhance how resources are allocated and boost patient results leading to overall cost efficiencies, in healthcare. Thus examining these aspects could offer perspectives on incorporating p16/Ki-67 and other markers into standard cervical cancer screenings.
Quality Assurance and Continuous Improvement
Healthcare facilities must have quality assurance procedures in place to uphold high standards in identifying cervical precancer cases accurately using p16/Ki-67 dual staining interpretation methods by staff members who undergo regular training and certification programs. Consistent monitoring of precision and patient results offers valuable insights for enhancing processes and outcomes through a culture of ongoing enhancement efforts, at clinics aimed at improving detection capabilities and promoting better overall health outcomes within their communities.
In conclusion, the incorporation of p16/Ki-67 biomarkers into cervical cancer screening protocols, alongside emerging molecular targets, represents a significant advancement in precision medicine. By adopting effective implementation strategies and engaging stakeholders, healthcare systems can enhance their cervical precancer detection capabilities. Leveraging solutions from reputable sources such as Celnovte will position clinics to efficiently utilize cutting-edge diagnostic technologies, ultimately leading to improved patient management and outcomes.
RELATED PRODUCTS