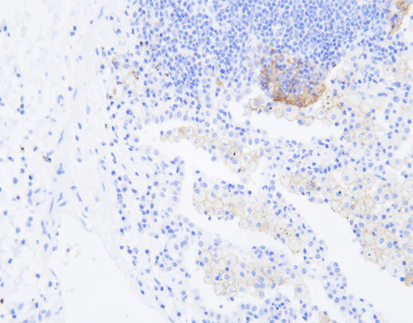
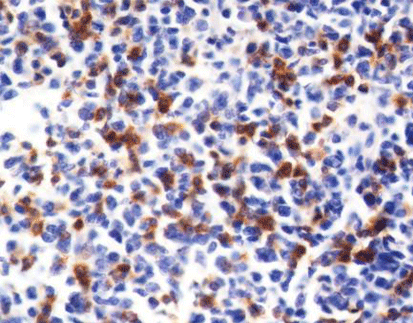
How to Interpret PD-L1 Positive Results in Cancer Diagnosis
2024-04-30
By admin
Understanding PD-L1 and Its Role in Cancer
PD-L1, also known as programmed death-ligand 1, plays a crucial role in the interaction between cancer cells and the immune system. Understanding its biology and function is essential for interpreting PD-L1 positive results in cancer diagnosis.
The Biology Behind PD-L1
PD-L1: A Key Player in Immune Response
Research has shown that PD-L1 acts as a critical regulator of immune responses by binding to its receptor, PD-1, on T cells. This interaction inhibits T cell activity, allowing cancer cells to evade immune surveillance and continue proliferating. The inhibition of T cell responses through the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has been identified as a major mechanism of tumor immune escape.
The PD-L1 Gene and Its Expression
The expression of the pdl1 gene is tightly regulated and can be influenced by various genetic and environmental factors. Studies have demonstrated heterogeneous expression of PD-L1 in circulating tumor cells (CTCs), circulating endothelial cells (CECs), and tumor tissues across different cancer types. For instance, statistical data has shown that 63% of patients had at least 1% positive PD-L1 cells, with 30% having at least 50% positive cells. These findings highlight the diverse expression patterns of PD-L1 within different patient populations.
PD-L1 in the Context of Cancer
How PD-L1 Affects Tumor Growth
Recent studies have indicated that high levels of PDL1 expression are associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and resistance to conventional treatments. Furthermore, research has revealed that intratumoral PDL1 RNA expression is present in a significant percentage of patients with specific genetic mutations, such as EGFR mutations.
The Role of PD-L1 in Evading Immune Detection
Scientific research findings have established that the interaction between PDL-1 on tumor cells and its receptor inhibits CD8 T cell cytotoxicity, thereby suppressing antitumor immune responses. This highlights the significance of understanding how PDL-1-mediated immune evasion contributes to tumor progression and impacts treatment outcomes.
Interpreting PD-L1 Positive Results
Interpreting PD-L1 positive results in cancer diagnosis involves understanding the significance of PD-L1 positivity and its impact on the diagnostic process. This section delves into the meaning of PD-L1 positivity, including testing and diagnostic criteria, as well as the influence of PD-L1 levels on cancer diagnosis.
The Meaning of PD-L1 Positivity
Understanding PD-L1 Testing
PD-L1 testing methods vary in terms of different clones, protocol conditions, instruments, and scoring/readout methods. These differences may pose challenges in introducing various PD-L1 assays for immunotherapy. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be aware of these variations when interpreting test results and making treatment decisions.
Criteria for PD-L1 Positive Diagnosis
The diagnostic accuracy of PD-L1 assays is a critical consideration. However, there is a lack of tools to measure the analytical sensitivity and specificity of immunohistochemistry assays, presenting a significant problem in assay development, methodology transfer, and daily monitoring of assay performance. Healthcare providers must navigate these challenges when interpreting PD-L1 positive results to ensure accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment plans.
The Impact of PD-L1 Levels on Diagnosis
High vs. Low PD-L1 Expression
When interpreting PD-L1 positive results, distinguishing between high and low levels of PDL1 expression is essential. Differentiating between these levels can provide valuable insights into the potential responsiveness to targeted therapies or immunotherapies. Understanding the nuances between high and low expression levels empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding patient care.
PD-L1 Positive and Its Prognostic Value
Sparse data are available on response rate and survival for patients tested with either cytology or histology materials for PD- L 1 expression. Additionally, different scoring methods exist for PD- L 1 IHC 22C3 PharmDx and subsequent protocols for treating gastric and other cancers. These factors underscore the complexity involved in interpreting PD- L 1 positive results accurately within the context of cancer diagnosis.
The Significance of PD-L1 Positive vs. Negative Results
Comparing PD-L1 Positive and Negative Diagnoses
When comparing PD-L1 positive and negative diagnoses, it is essential to consider the implications of PD-L1 negativity and the clinical relevance of PD-L1 status in cancer diagnosis.
Implications of PD-L1 Negativity
PD-L1 negativity in cancer patients may indicate a potential lack of response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody therapy. Studies have shown that patients with low or absent pdl1 expression on cancer cells are less likely to benefit from immunotherapy treatment. This highlights the significance of accurately assessing PD-L1 status to determine the most effective treatment approach for individual patients.
The Clinical Relevance of PD-L1 Status
The clinical relevance of PD-L1 status lies in its predictive value for treatment response and patient outcomes. Research has demonstrated that high levels of PDL1 expression correlate with improved response rates in certain cancer types, indicating a potential benefit from anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Conversely, low or absent pdl 1 expression may suggest a lower likelihood of response to immunotherapy, guiding healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions based on individual patient profiles.
PD-L1 Status and Treatment Decisions
Understanding how PD-L1 influences treatment choices is crucial for personalized medicine and optimizing patient care.
How PD-L1 Influences Treatment Choices
PD-L1 status serves as a critical biomarker for determining the most suitable treatment approach for cancer patients. For individuals with high PDL- L 1 expression, targeted immunotherapies such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors may offer significant therapeutic benefits by enhancing antitumor immune responses. On the other hand, patients with low or absent pd l 11 expression may require alternative treatment modalities tailored to their specific molecular profiles and disease characteristics.
The Role of PD-L1 in Personalized Medicine
In the era of personalized medicine, integrating PD-L1 status into treatment decision-making processes enables healthcare providers to deliver tailored therapies that align with each patient’s unique biological markers. By leveraging information about pd l 11 expression levels, clinicians can optimize treatment strategies, minimize adverse effects, and maximize therapeutic efficacy, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The association between pd-l 11 expression and clinical outcomes underscores the importance of incorporating this biomarker into comprehensive diagnostic assessments and therapeutic considerations for cancer patients.
Navigating Treatment Options for PD-L1 Positive Cancer
After receiving a positive PD-L1 diagnosis, navigating treatment options becomes a critical aspect of the patient’s journey. Understanding the available targeted therapies and the future of PD-L1 positive cancer treatment is essential for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Targeted Therapies for PD-L1 Positive Patients
Immunotherapy and PD-L1 Inhibitors
PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors have emerged as effective treatments for several types of cancer. These inhibitors act by blocking the association of PD-L1 with its receptor, PD-1, thereby unleashing the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. Clinical studies have demonstrated sustained survival benefits in multiple tumors, making them a promising frontline treatment option for patients with high PDL- L 1 expression.
However, it is important to note that while these inhibitors have shown significant efficacy, only a minority of patients experience prolonged and sustained curative responses to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade treatment. Therefore, ongoing research aims to identify new biomarkers predictive of treatment benefits beyond PD-L1 and tumor mutational burden (TMB) levels. This pursuit reflects the evolving landscape of personalized medicine in oncology.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
In addition to established immunotherapies, ongoing clinical trials are exploring novel treatment modalities for PD-L1 positive cancer. These trials aim to uncover alternative therapeutic approaches that can further improve patient outcomes. Notably, recent studies have investigated the significance of different forms of extracellular PD-L1 as a potential biomarker for cancer management. Additionally, researchers are exploring how exosome production could be targeted to benefit patients who do not respond to traditional immunotherapies.
The Future of PD-L1 Positive Cancer Treatment
Advances in PD-L1 Research
The interaction between PD- L 11 and its receptor has been a focal point in cancer immunotherapy research. Significant strides have been made in understanding the complexities of this interaction and its implications for treatment outcomes. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of diverse expression patterns of PD- L 11, shedding light on its potential as a prognostic indicator across various cancer types.
Moreover, investigations into immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD- L 11 have presented revolutionary therapeutic approaches for specific cancers such as non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These inhibitors have demonstrated durable overall survival benefits in advanced lung cancer cases, underscoring their potential as transformative treatments.
The Potential for Combination Therapies
As research continues to unravel the intricacies of PD- L 11 expression and its impact on treatment response, there is growing interest in combination therapies that leverage multiple treatment modalities simultaneously. The exploration of combination therapies represents an exciting frontier in oncology, offering the possibility of enhanced treatment efficacy through synergistic mechanisms.
Furthermore, ongoing efforts seek to identify new strategies that target immune checkpoints beyond PD- L 11, aiming to expand the proportion of responsive cases across multiple types of cancers. This endeavor aligns with the broader goal of advancing precision medicine by tailoring treatments based on individual molecular profiles and disease characteristics.
Celnovte Biotechnology Co., Ltd, a leading company in the field of pathological diagnostic reagents and instruments, could be a valuable resource for interpreting PD-L1 positive results in cancer diagnosis. Founded in 2010 and headquartered in Zhengzhou, China, Celnovte has a strong presence in the global market with over 600 units of fully automated IHC stainers installed worldwide since their launch in 2018.
Celnovte‘s portfolio includes market-leading Immunohistochemistry and in-situ hybridization technologies. Their MicroStacker™ IHC detection system is known for its exceptional sensitivity and specificity, while their PolyStacker™ technology can significantly reduce the turnaround time of frozen section IHC experiments to as short as 10 minutes. Additionally, their SuperISH™ RNA in-situ hybridization technology enables detection of RNA targets at the single molecular level and single cell resolution.
These technologies could potentially provide valuable insights into the interpretation of PD-L1 positive results in cancer diagnosis. PD-L1, or programmed death-ligand 1, is a protein that has been associated with several types of cancer. Understanding its presence and distribution in cancerous tissues can be crucial for determining the most effective treatment strategies.
Celnovte’s mission is to elevate precision in cancer diagnostics and enrich patients’ lives through innovative products and services. Their commitment to product quality, customer satisfaction, scientific innovation, and organizational excellence makes them a reliable partner in the field of cancer diagnostics.
Conclusion
Summarizing Key Takeaways
In conclusion, the significance of PD-L1 in cancer diagnosis and treatment cannot be overstated. The understanding of PD-L1 expression levels and their implications for patient outcomes is crucial for guiding personalized treatment decisions and improving clinical management.
Peter Schmid, co-lead investigator of a phase III trial, emphasized that PD-L1 proved to be a biomarker of benefit from therapy. This underscores the importance of PD-L1 as a predictive indicator for treatment response, shaping the landscape of precision medicine in oncology.
Studies on PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors have revealed that these agents are associated with significantly prolonged overall survival in both patients that were PD-L1 positive and PD-L1 negative. However, the efficacies of PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade treatment in these patient groups were significantly different, highlighting the impact of PD-L1 status on treatment outcomes.
Moreover, research on the prevalence of PD-L1 expression in tumor cells has shed light on its association with clinicopathological characteristics and its potential role in guiding immune-oncologic treatment decisions. The fluctuation of PD-L1+ CTCs/CECs during therapy further emphasizes the dynamic nature of PD-L1 expression and its relevance in monitoring treatment responses.
The first clinical trial of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors marked a pivotal moment in cancer therapeutics, leading to subsequent advancements and approvals for various forms of cancer. This exemplifies the transformative potential of targeting immune checkpoints such as PD- L 11, paving the way for innovative combination therapies and precision medicine approaches.
Empowering Patients through Knowledge
Empowering patients with knowledge about PD-L1 positivity equips them to actively participate in shared decision-making processes regarding their treatment options. By understanding the implications of their PD-L1 status, patients can engage with healthcare providers to explore tailored therapies aligned with their unique molecular profiles.
Access to information about emerging treatments and ongoing clinical trials provides patients with hope and optimism for improved outcomes beyond conventional modalities. This knowledge empowers individuals to advocate for comprehensive diagnostic assessments that encompass PD-L L 11 expression analysis, fostering informed discussions about personalized care plans.
Furthermore, raising awareness about the significance of PD- L 11 in cancer diagnosis fosters a sense of agency among patients, encouraging proactive involvement in their healthcare journeys. As advancements continue to unfold in PD- L 11 research, patient education remains pivotal in promoting informed decision-making and cultivating a supportive healthcare environment.