Exploring PAS Staining: Key Applications in Pathological Diagnosis

By admin
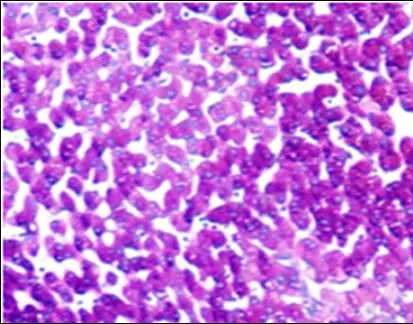
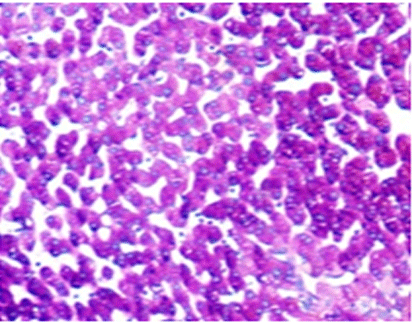
Periodic Acid-Schiff (referred to as PAS staining) an employed histological method enables the detection and display of particular carbohydrates like glycogen and mucopolysaccharides in tissue samples by utilizing specific chemical reactions, for diagnostic purposes.
Chemical Reactions Involved
Staining with PAS includes the process of oxidizing carbohydrates, with acid to create aldehyde groups that later interact with Schiff reagent to form a magenta color and reveal carbohydrate-rich structures in tissues.
Visualizing Glycogen and Mucopolysaccharides
Using the PAS stain is great for showing glycogen and mucopolysaccharides because it works well with these substances specifically. This staining method results in a color shift which helps pathologists pinpoint regions, with high levels of these carbohydrates; this makes it easier for them to delve deeper into their analysis and diagnosis process.
Importance of PAS Staining in Pathology
PAS staining plays a crucial role in pathology due to its ability to differentiate between tissue types and highlight abnormal cellular components.
Differentiating Tissue Types
PAS staining is commonly used to differentiate between tissue types by assessing their carbohydrate levels helping in the identification of normal and abnormal tissue conditions in samples.
Highlighting Abnormal Cellular Components
PAS staining not only helps distinguish between tissues but also plays a crucial role in drawing attention to irregular cellular elements that could signify underlying health issues or diseases—a feature that renders it invaluable, for identifying various pathological conditions.
How is PAS Staining Applied in Diagnosing Diseases?
Role in Identifying Glycogen Storage Diseases
PAS staining is particularly useful in diagnosing glycogen storage diseases by revealing diagnostic markers indicative of glycogen accumulation.
Diagnostic Markers for Glycogen Accumulation
Glycogen storage diseases are characterized by excessive glycogen buildup within cells. PAS staining highlights this accumulation through its distinct color change, serving as a critical marker for diagnosis.
Case Examples in Clinical Practice
Clinical practice has demonstrated the efficacy of PAS staining in identifying glycogen storage diseases. For instance, liver biopsy samples from patients can be analyzed using this technique to confirm diagnoses based on observed glycogen deposits.
Detection of Fungal Infections Using PAS Staining
Another application of PAS staining is in detecting fungal infections by recognizing characteristic fungal structures within tissues.
Recognizing Fungal Structures
Fungal organisms contain polysaccharide-rich cell walls that react with the PAS stain, allowing them to be visualized under a microscope. This feature aids pathologists in accurately identifying fungal infections.
Benefits Over Other Staining Techniques
Compared to other methods, PAS staining offers advantages such as enhanced visibility and specificity when detecting fungal elements. These benefits make it a preferred choice for diagnosing mycotic infections.
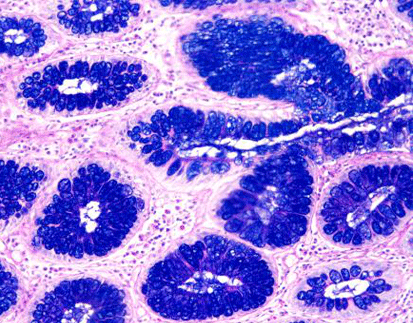
Application in Renal Pathology
PAS staining also finds application in renal pathology by identifying changes in basement membranes associated with kidney diseases.
Identifying Basement Membrane Changes
Alterations in the basement membrane structure are indicative of various renal pathologies. The use of PAS stain helps reveal these changes, providing insights into disease progression and severity.
Correlation with Clinical Outcomes
By correlating observed basement membrane changes with clinical outcomes, healthcare professionals can better understand patient prognosis and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Why Choose PAS Staining for Your Laboratory?
Advantages Over Alternative Methods
When considering diagnostic techniques, PAS staining presents several advantages over alternative methods due to its specificity, sensitivity, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency.
Specificity and Sensitivity Comparisons
PAS staining demonstrates high specificity and sensitivity levels compared to other histological stains. This precision ensures accurate detection and differentiation of pathological features within samples.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
The cost-effectiveness and efficiency associated with PAS Staining make it an attractive option for laboratories seeking reliable diagnostic solutions without incurring excessive expenses or time delays.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy with PAS Staining Kits
To further enhance diagnostic accuracy, laboratories can utilize specialized kits designed for optimal performance during routine procedures.
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Staining Kit
These kits provide standardized reagents that ensure consistent results across different samples while minimizing potential errors during processing steps. By integrating these kits into laboratory workflows, accuracy levels are significantly improved.
Integration into Routine Lab Procedures
Integrating Solutions like the Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Staining Kit into routine lab procedures streamlines operations while maintaining high-quality standards throughout diagnostic processes—ultimately leading to better patient care outcomes through precise diagnoses delivered promptly upon sample analysis completion.
Solutions for Implementing PAS Staining in Your Practice
Solutions for Streamlining Laboratory Processes
Implementing PAS staining into your laboratory practice requires a strategic approach to optimize efficiency and accuracy. By adopting comprehensive solutions, you can streamline laboratory processes, ensuring that PAS staining is performed consistently and effectively. Integrating automated staining systems can help lessen work and decrease human mistakes in the process. Moreover by standardizing protocols, throughout the lab the consistency of results is improved, which boosts the dependability of findings.
Implementing cutting-edge technologies and software solutions in the workplace can enhance productivity by offering data analysis and tracking features This combination enables smooth interaction, among various departments within the laboratory setting which helps in making faster decisions and boosting operational effectiveness as a whole.
Training and Support for Optimal Results
For the outcomes using PAS staining methods, it’s vital to provide consistent training and assistance to lab workers. Ongoing learning initiatives help staff stay current on trends, in staining methods and diagnostic uses. Training sessions and talks hosted by industry specialists advise on resolving common problems and adopting effective approaches.
Additionally setting up a strong supportive network in the lab encourages teamwork and the exchange of ideas among colleagues. This strategy not only boosts individual skills but also enriches the team’s combined knowledge base, resulting in higher accuracy, in diagnosis, and better patient outcomes in the end.
What Future Developments Can We Expect in PAS Staining?
Innovations in Staining Techniques
Exciting changes are on the horizon, for PAS staining as new methods are being developed to improve its ability to diagnose conditions accurately and precisely identify abnormalities by targeting carbohydrate structures more effectively with innovative reagents.
Furthermore, combining imaging technologies with PAS staining enables pathologists to view tissue samples in high resolution, providing detailed information on cellular morphology, and helping them identify subtle pathological changes that might go unnoticed, with conventional methods.
Potential Expansions into New Diagnostic Areas
Researchers are constantly discovering uses for PAS staining and exploring its potential in uncharted diagnostic territories is promising! One area of interest is its potential in cancer detection, by pinpointing specific carbohydrate markers linked to malignancy during ongoing studies.
Moreover, PAS staining could be utilized in healthcare to provide valuable information on individual patient characteristics determined by carbohydrate expression trends. This method has the potential to pave the way, for customized treatment plans that enhance treatment effectiveness and reduce side effects.
By keeping up to date with advancements, in the field of diagnostics laboratories can place themselves at the forefront of innovative healthcare solutions to effectively address changing medical requirements.
RELATED PRODUCTS