Decoding IHC Stainer: Key Differences in ICC and IHC Staining
2024-12-24
By admin
Have you ever wondered how scientists observe proteins in cells and tissues visually? Immunocytochemistry (ICC) and Immunohistochemistry (IHС) are methods in molecular pathology that aid researchers in identifying particular proteins with the help of antibodies. Even though both techniques have similarities between them; they serve purposes. Provide valuable perspectives into the structures of cells and tissues. In this blog post, we will delve into the distinctions between ICC and IHC, their uses, and why selecting the appropriate approach is crucial for your research endeavors.
What are ICC and IHC Staining Techniques?
In the field of pathology, it is crucial to grasp the distinctions between staining methods for precise diagnosis and research purposes. Immunocytochemistry (ICC ) and Immunohistochemistry ( IHC ) are two approaches used to observe proteins in cells and tissues. While both methods rely on antibodies to identify antigens they vary considerably in their use and techniques. As you explore these methods it is important to recognize their characteristics and advantages.
Overview of ICC Staining
Immunocytochemistry, commonly known as ICC is a method mostly employed to identify proteins within cells useful in the examination of cultured cells or cell suspensions.
Fixing cells onto a slide
Blocking non-specific binding sites
Incubating with primary antibodies that target specific proteins
Using secondary antibodies conjugated with enzymes or fluorophores for detection
ICC enables the mapping of proteins within cells and facilitates the in-depth examination of functions at a microscopic level.
Overview of IHC Staining
In contrast, Immunohistochemistry ( IHC ) is used to detect protein expression in tissue sections. This method preserves the structure of tissues. Provides information on how proteins are distributed spatially in various types of tissues. The process of IHC includes ;
Fixing tissue samples
Sectioning tissues onto slides
Blocking non-specific sites
Applying primary antibodies followed by enzyme or fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies
In fields, like cancer research and histopathology, the importance of IHC lies in its capacity to maintain tissue structure intact.
How Do ICC and IHC Differ in Methodology?
Both ICC and IHC have the goal of identifying antigens through antibody detection but their approaches differ based on the types of samples and preparation methods used – a key factor in deciding the most suitable method for each application.
Sample Preparation Techniques
The ICC process of sample preparation emphasizes the treatment of cells rather than bulk samples. Then treated with solutions like paraformaldehyde to fix them in place. Additionally, they may be permeabilized to allow for access for antibodies targeting components without causing any harm to the cell structure.
On the other hand, Immunohistochemistry (IHC) involves working with tissue samples. The tissues are preserved in paraffin or frozen material before being cut into sections. These thin slices go through steps, like removing paraffin (when needed) exposing antigens to reveal their structure, and fixing the tissue to maintain its shape and form.
Detection Methods Employed
In ICC identifying substances often requires the use of fluorescence microscopy because of its precise detection capabilities and accuracy levels are usually high, in this method of analysis.
Traditional IHC methods often use detection techniques, like HRP DAB systems that enable examination through microscopes. A method reminiscent of chromogenic in situ hybridization technology for RNA detection using comparable systems.
Why Choose IHC Stainer for Specific Applications?
Choosing the staining method depends on what you’re looking for in your research and the results you want to achieve The IHC stainer stands out as a tool for some purposes because of its unique benefits compared to other techniques.
Advantages of Using IHC Stainer
The IHC stainer offers several benefits:
Preservation of tissue architecture allows comprehensive analysis of protein distribution across different tissue regions.
Chromogenic detection provides clear results observable under standard light microscopes.
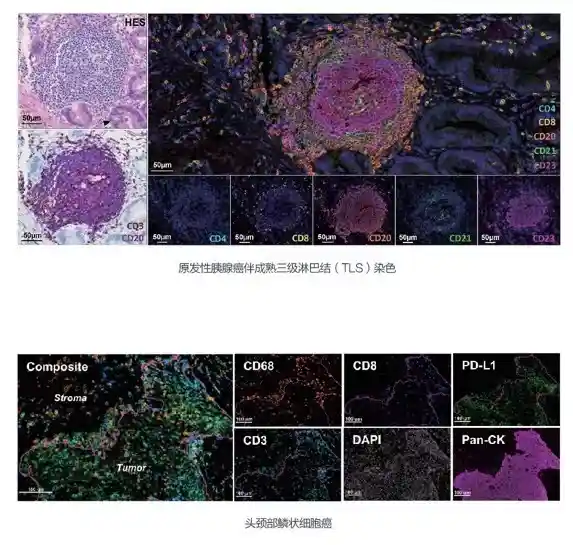
Multiplexing capabilities enable simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers within a single section—critical for complex biological studies like cancer research.
The characteristics of the IHC stainer make it especially well suited for tasks that require a focus on the context within tissues.
Limitations to Consider
.It’s crucial to keep in mind constraints when using an IHC stainer. The potential for non-specific binding necessitates careful optimization of blocking steps.
Chromogenic substrates may lack the sensitivity offered by fluorescence-based methods.
It’s important to know these boundaries to make the most of IHC staining’s advantages and overcome any obstacles that may arise.
An examination of these factors and their implications in areas of research study to uncover new perspectives on the effective implementation of ICC and IHC staining methods for more accurate molecular analysis capabilities.
How Does Celnovte Stand Out as an IHC Stainer Supplier?
When choosing a provider for IHC staining equipment and supplies, it is important to look at things like their reputation and the variety of products they offer alongside how reliable they’re in delivering these services or products to customers. Celnovte stands out from its competitors by focusing on these aspects which guarantee that scientists get top-notch products and services designed to meet their requirements.
Reputation and Reliability
Over time Celnovte has established itself as a name in the pathology sector by consistently providing dependable IHC staining solutions that meet the rigorous demands of research and clinical diagnostics. Their products showcase a dedication to excellence through their performance and reliability reassuring researchers and clinicians of reproducible results essential for extended studies and diagnostic uses.
Consistent Product Quality: Celnovte’s rigorous quality control measures guarantee that each batch of reagents meets high standards, minimizing variability in staining outcomes.
Trusted by Experts: The company’s reputation is reinforced by endorsements from leading researchers and institutions who rely on their products for accurate immunohistochemical analyses.
Product Offerings
Celnovte provides a variety of IHC staining solutions to meet research requirements . Their lineup consists of cutting-edge immunofluorescence kits that allow for the identification of several biomarkers in one tissue sample. This feature proves beneficial in biological investigations that necessitate a grasp of the spatial arrangement of different proteins.
Advanced Multiplexing Kits: These kits provide superior signal-to-noise ratios and clearer results, facilitating deeper insights into complex biological systems like cancer research and immunology.
Ease of Integration: Celnovte’s products are designed for seamless integration into existing workflows, whether using automated platforms or manual techniques. This adaptability ensures minimal disruption during transition phases.
FAQs on ICC and IHC Staining
Exploring the complexities of ICC and IHC staining can prove to be quite a puzzle for individuals in this field of study! In this discussion, we delve into asked questions to shed light on the uses and important factors to consider when applying these techniques.
What are the primary differences between ICC and IHC staining?
Both ICC and IHC tests that use antibodies to detect antigens differ mainly in the type of sample. How they are applied.
ICC (Immunocytochemistry)focuses on individual cells, often used with cultured cells or cell suspensions. It provides detailed localization at the cellular level.
IHC (Immunohistochemistry)involves tissue sections, preserving tissue architecture to study protein distribution across different regions.
The variances determine when to use them; ICC is great for studying cells while IHC shines in researching tissues.
Can the same antibodies be used for both ICC and IHC?
There are cases where antibodies might work for both ICC and IHC tests. However multiple factors come into play in situations.
Antibody Specificity: Antibodies must specifically bind to target antigens without cross-reactivity.
Validation Across Applications: Antibodies should be validated for use in both cell-based (ICC) and tissue-based (IHC) contexts to ensure reliable results.
When choosing antibodies for dual use situations, researchers need to consider these factors.
How do environmental factors influence staining outcomes?
The staining outcomes in both ICC and IHC can be greatly affected by factors.
Temperature: Variations can affect antibody binding efficiency and enzyme activity during detection steps.
Humidity Levels: High humidity may lead to excessive background staining or reduced signal intensity.
Maintaining a staining quality is facilitated by controlling these variables using designed protocols in place following the recommended guidelines provided by suppliers such as Celnovte to minimize any external factors affecting the results of experiments.
By answering these questions that people often ask about ICC and IHC staining methods in research settings, you enhance your grasp of how to utilize these techniques for your scientific investigations. This awareness enables you to make informed choices when choosing the suitable approaches for your particular research questions.