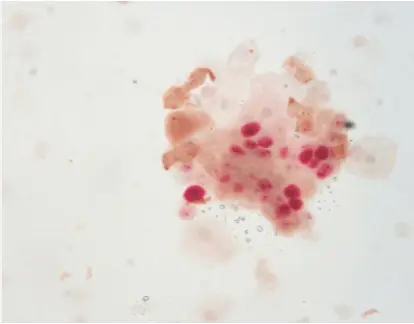
A Game-Changer in Histopathology: p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining

By admin
Biomarkers have become essential in histopathology as they provide information about cellular activities and health conditions within tissues and organs. Two noteworthy biomarkers in focus are p16 and Ki-67 due to their significance, in regulating cell cycles and proliferation rates. These markers offer insights that help us comprehend how tumors develop and advance over time.
The Importance of p16 and Ki-67
P16 is a type of protein that helps regulate cell growth by blocking enzymes responsible for cell division in the body system; serving as a safeguard, against tumor formation when functioning properly in healthy cells. Conversely, Ki-67 is another protein found inside cell nuclei known to be linked with cell reproduction; thus serving as a crucial indicator of active cell growth often used to gauge the progression of tumors.
How Dual Staining Enhances Diagnostic Accuracy
Enhancing accuracy is achieved through dual staining with p16 and Ki-67 where both critical biomarkers are assessed on one tissue sample simultaneously to minimize errors in diagnosis and improve detection rates, in cervical cancer screening procedures. By providing clear, objective results through color interpretation, dual staining minimizes subjective biases that can affect traditional methods.
Comparing p16/Ki-67 with Traditional Methods
Limitations of Conventional Staining Techniques
Conventional methods of staining typically depend on evaluating one marker at a time when examining behavior. This approach may not provide an assessment and could result in incomplete conclusions due to its limited sensitivity and specificity. Moreover, the traditional techniques are often labor intensive. Could be prone to human error, in the interpretation process.
Advantages of Dual Staining in Clinical Practice
Dual staining offers several advantages over traditional methods. Examining biomarkers at the same time and positively enhancing diagnostic accuracy is showcased through this method of analysis. This strategy is not as influenced by judgment which results in more uniform outcomes among various labs and medical professionals. Moreover، using staining could simplify procedures by minimizing the requirement, for numerous tests.
How Does p16/Ki-67 Staining Work?
The Mechanism Behind Dual Staining
The technique of staining includes utilizing specialized antibodies to identify p16 and Ki-67 proteins in cells or tissue samples simultaneously on one slide, for precise evaluation of their expression levels.
Interaction Between p16 and Ki-67 Proteins
p16 and Ki-67 proteins interact within the cellular environment to provide insights into cell cycle dynamics. While p16 inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases to halt cell division, Ki-67 marks actively dividing cells. Their combined evaluation through dual staining offers a comprehensive view of cellular proliferation status.
Technical Aspects of Implementing Dual Staining
Implementing dual staining requires precise technical execution to ensure accurate results. It involves using specialized reagents such as the P16/Ki-67 Dual Staining Detection Kit, which simplifies the process by providing all necessary components for successful staining.
Applications in Clinical Diagnosis
Cervical Cancer Screening and Its Implications
p16/Ki-67 dual staining has significant implications for cervical cancer screening. It improves detection rates by identifying precancerous lesions with greater accuracy than traditional cytology alone. This method reduces false negatives and enhances early intervention opportunities.
Broader Applications in Oncology
In addition to screening for cancer, the p16/Ki-67 dual staining method has broader uses in different areas of oncology. Its capacity to assess tumor growth is beneficial, in diagnosing cancers where cell cycle abnormalities are involved.
Solutions
For laboratories seeking efficient implementation of dual staining techniques or exploring other innovative solutions in histopathology, Celnovte offers comprehensive resources tailored to meet clinical needs effectively. Their Solution Center provides guidance on integrating cutting-edge technologies into existing workflows while ensuring optimal diagnostic outcomes.
Why Should You Consider p16/Ki-67 Staining?
Benefits for Pathologists and Clinicians
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency in Diagnosis
Incorporating p16/Ki-67 staining into procedures greatly boosts precision and speediness. Together assessing these biomarkers aids pathologists in grasping cellular dynamics thoroughly in one examination. This method of staining lessens errors in diagnosis and speeds up diagnoses making quick decisions feasible, in medical scenarios.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
Clinicians benefit from using p16/Ki-67 staining to improve outcomes by identifying precancerous lesions more accurately and enabling early intervention strategies that may help prevent diseases like cervical cancer from advancing further quickly and efficiently. This proactive method not only boosts patient care but also streamlines resource distribution, in healthcare systems by reducing unnecessary treatments and follow-ups.
Solutions for Implementing Dual Staining
Accessing the Latest Technology and Kits
Implementing dual staining techniques requires access to advanced technology and specialized kits. Laboratories can benefit from utilizing products like the P16/Ki-67 Dual Staining Detection Kit, which streamlines the staining process by providing all necessary reagents in one package. This kit ensures consistent results across different samples and laboratories, supporting reliable diagnostics.
What Does the Future Hold for Histopathology?
Innovations Driven by p16/Ki-67 Research
Potential Developments in Diagnostic Tools
Advancements in tools are being fueled by research into p16/Ki‐67 markers. The ongoing study of these biomarkers could result in improved assays with accuracy in the detection and monitoring of different types of cancer. This progress has the potential to transform how cancers are identified and managed opening doors for tailored treatment approaches.
Integration with Other Emerging Technologies
The integration of p16/Ki-67 research with other emerging technologies presents exciting possibilities for histopathology. Combining dual staining with digital pathology platforms or artificial intelligence could further enhance diagnostic accuracy by providing automated analyses and reducing human error. This synergy between technologies promises to transform how pathologists interpret complex data sets.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
Addressing Practical Implementation Issues
Despite its benefits are clear. There are some issues with using p16/Ki-67 staining which includes ensuring consistency across different labs and training staff on new techniques to use this method effectively this is a crucial step to overcome these challenges and it requires teamwork among researchers doctors and industry players to set up rules, for uniformly using this technique globally.
Opportunities for Further Research and Collaboration
The histopathology field is currently at a point with numerous research possibilities on the horizon for exploration and advancement. Investigating p16/Ki-67 biomarkers through collaborative initiatives involving academic institutions, healthcare providers and industry pioneers has promising potential to expedite discoveries. Focused collaborations, on research could lead to revealing novel understandings of tumor biology that might revolutionize cancer diagnostics.
In conclusion, embracing innovations like p16/Ki-67 staining represents a pivotal step forward in histopathology practices. For those seeking effective solutions tailored to modern clinical demands, exploring resources provided by Celnovte can facilitate the seamless integration of cutting-edge technologies into existing workflows while enhancing overall diagnostic capabilities.
RELATED PRODUCTS