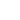 PRODUCT CATEGORY
PRODUCT CATEGORY
CONTACT US
Product Features
-
Principle
N,N-dimethyl-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride and N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine
dihydrochloride are both ammonium salts that have a positive charge when dissociated. The
diammonium salt is combined with sulfated acid mucins to form a complex, which can be observed
through a color change. The reaction is slow, and Ferric chloride is used as a catalyst to speed up
staining. On one hand, the oxidation of the two ammonium salts forms a brown-black cationic
chromogen, which speeds up staining. On the other hand, the pH of the stain solution decreases to
1.4. At this pH value, only the sulfate group reacts with the diammonium salt to form a complex of
purple-brown to brown-black, as the carboxyl group on the section cannot combine with the
diammonium salt. Subsequently, Alicin blue (pH 2.5) stains the carboxylated sialic acid mucus as
blue, allowing the acidic mucus of the two main groups to be shown separately.
-
Features
a) High specificity
b) Simple to operate
c) Easy to identify
Specification
|
Reagent |
Main Component |
|
|
HID- solution |
N,N-dimethyl-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride, N, N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride |
|
|
Ferric chloride solution |
Ferric chloride |
|
|
Alcian blue solution |
Alcian blue solution |
|
Note: Each component of this product cannot be used separately, and components from different
batch numbers cannot be used interchangeably.
More Info
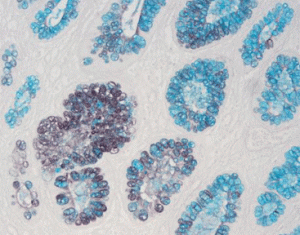
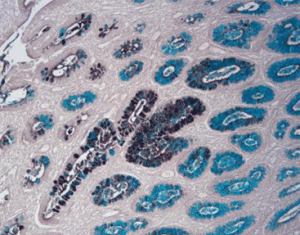
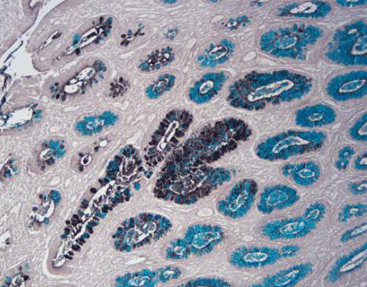
Results Interpretation
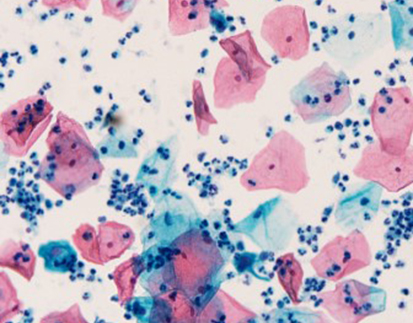
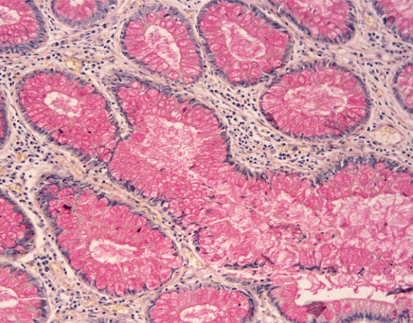
After staining, the color presentation of sulfated acid mucins ranges from purplish brown to brown-black. The carboxylated acid mucins appear blue. The cell nucleus remains unstained.
20X
10X
Related Product













 Chat
Chat
 message
message

 Quote
Quote

 Download
Download