PRODUCT CATEGORY
PRODUCT CATEGORY
CONTACT US



6 Cuizhu St, Zhong Yuan Qu, Zheng Zhou Shi, He Nan Sheng, China, 450001
Factor XIIIa(EP3372), RMab
Factor XIIIa, also known as fibrinoligase and fibrin stabilizing factor, is the last enzyme that occurs in the coagulation cascade. It is a calcium-dependent transglutaminase or aminotransferase. Factor XIIIa is involved in the coagulation mechanism and also has the effect of stabilizing the molecular surface and membrane of cells. Factor XIIIa is detected in normal skin and inflammatory skin. XIIIa-positive cells present in the skin as a specific bone marrow dermal dendritic cell population, which is very different from Langerhans cells in the skin and shares some common features of mononuclear macrophages. In the case of benign skin lesions such as inflammatory atopic eczema and psoriasis, factor XIIIa positive cells increase in the upper part of the dermis, which is closely related to lymphocytes.
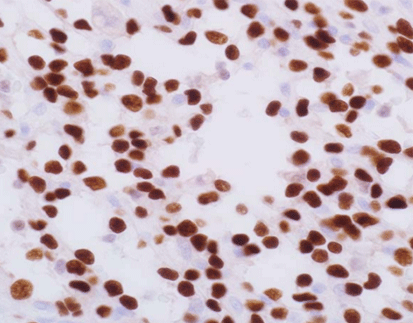
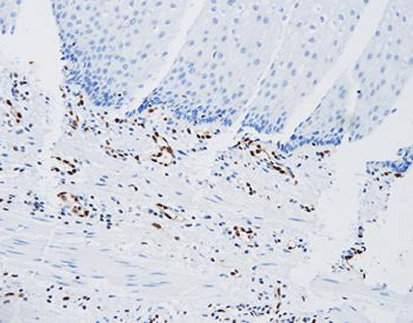
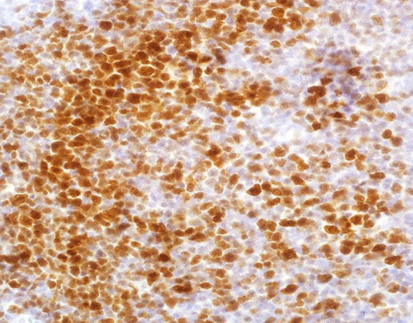
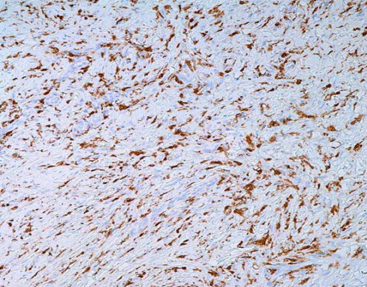
Staining Tissue
[As Figure shows]
Neurofibroma tissue stained with Factor XIIIa
[Intended Use]
Factor XIIIa, also known as fibrinoligase and fibrin stabilizing factor, is the last enzyme that occurs in the coagulation cascade. It is a calcium-dependent transglutaminase or aminotransferase. Factor XIIIa is involved in the coagulation mechanism and also has the effect of stabilizing the molecular surface and membrane of cells. Factor XIIIa is detected in normal skin and inflammatory skin. XIIIa-positive cells present in the skin as a specific bone marrow dermal dendritic cell population, which is very different from Langerhans cells in the skin and shares some common features of mononuclear macrophages. In the case of benign skin lesions such as inflammatory atopic eczema and psoriasis, factor XIIIa positive cells increase in the upper part of the dermis, which is closely related to lymphocytes.
[Specifications]
| Product Name | Factor XIIIa(EP3372), RMab |
| Catalog No. | CFR-0010 |
| Intended Use | IVD, RUO |
| Species Reactivity | Human; others not tested |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm / Nucleus |
| Antibody Type | Rabbit Monoclonal |
| Clone | EP3372 |
| Format and Volume | Ready-to-use: 1mL, 3mL, 6mL Concentrated: 0.1mL, 0.2mL and 1mL |
[Datasheets & SDS]
| IVD Datasheet (IFU) | ↕️ Download |
| RUO Datasheet (IFU) | ↕️ Download |
| SDS sheet | check with sales |
[Storage and Validity]
Store at 2~8°C. Avoid freezing.
Maintain temperature below room temperature during transport, ensuring it does not exceed one week.
Related Product







 PRODUCT CATEGORY
PRODUCT CATEGORY


 Chat
Chat
 message
message

 Quote
Quote