PRODUCT CATEGORY
PRODUCT CATEGORY
CONTACT US
EBER Probe (Manual)
With the deeper realizing about EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus, EBV), it has attracted more and more attention. EBV is also known as human herpes virus type 4 (HHV-4).
Researches show that 95% of people worldwide have been infected with the virus. People who are infected with the virus first are asymptomatic, but a few can develop infectious mononucleosis. Once infected, EBV will be lurking in human B cells, and the infected people will become a lifelong carrier. The study found that latent EBV is not static, but has been carrying out slow biological activities. In a few specific cases, EBV can also change from a latent state to a proliferating state. Latent EBV infection is related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma and lymphoid tissue diseases (Hodgkin's lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, NK/T cell lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic lymphoma, enteropathy T cell lymphoma, lymphoid granuloma, infectious mononucleosis, etc.). Once infected with EBV, the infected people will carry the virus for life. EBV has the characteristics of infection and transformation of B cells, which can transform small lymphocytes into immortal lymphoblastoid cells.
There are 11 kinds of EBV latent gene expression now: core antigens (EBNA-1, EBNA-2, EBNA-3A, 3B, 3C, EBNA-LP), latent membrane proteins (LMP-1, LMP2A, 2B), and short mRNA (EBNA-1 and EBER-2). According to the expression of EBV in different tumors, it is currently divided into three types: latent type I (EBNA-1 and EBERs), latent type II (EBNA-1, LMP-1, -2A, -2B, EBERs), and latent III (EBNA-1, -2, -3A, -3B, 3C, -LP, LMP-1, -2A, -2B, EBERs).
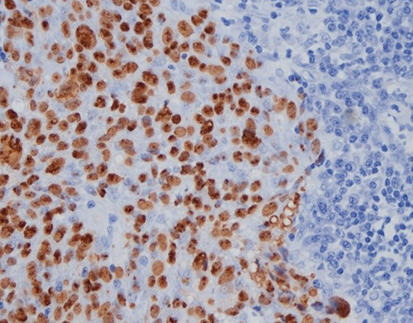
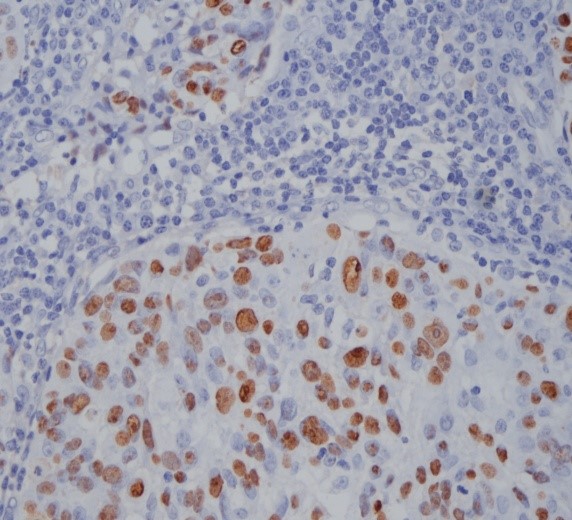
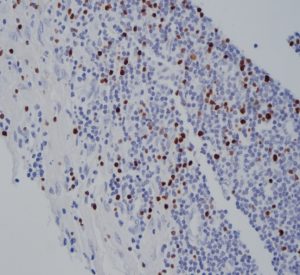
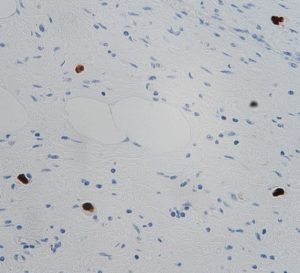
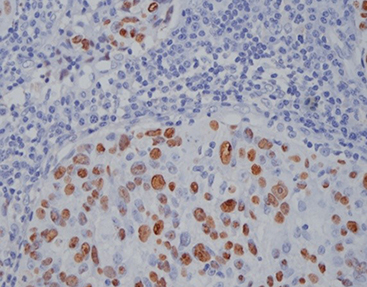
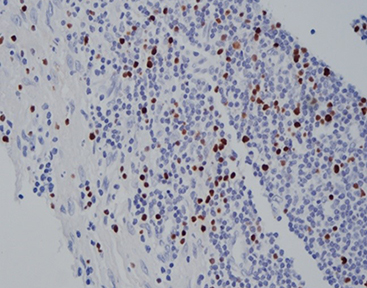
When determining the relationship between EBV and disease, EBER in situ hybridization has become a recognized standard method.
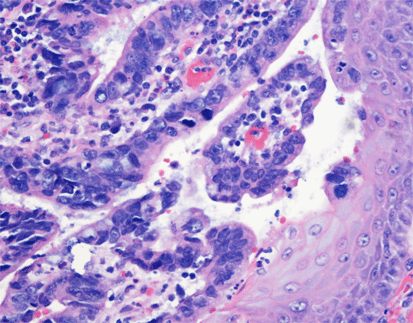
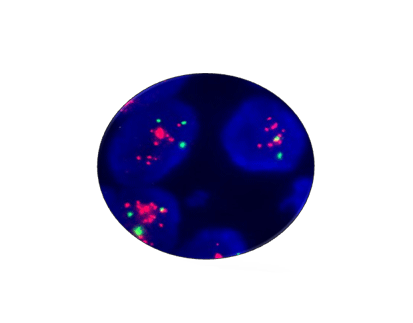
The EBER probe is a DNA probe labeled with digoxin, which can specifically bind to EBER1 and EBER2. It has high specificity and sensitivity.
Product Features
- EBER Probe-Manual Reagents
Specification
|
EBER Probe |
Code |
Classification |
Specification |
|
CF6001 |
Manual |
25T/50T/100T |
Staining Photos (Manual)
|
Main Components |
|||
|
EBER Probe |
Polymer |
Pepsin working solution |
Tween-20 |
|
Anti-digoxin antibody |
DAB Substrate |
Hematoxylin staining solution |
EBER Positive Control |
|
Linker |
DAB Buffer |
PBS |
DAB Enhancer |
More Info
Clinical Significance of EBER Detection:
- Find the cause: Distinguish whether it is latent infection of EBV or disease state caused by EBV infection.
- Identify non-neoplastic diseases such as infectious mononucleosis and chronic active EBV infection.
- Differential diagnosis of neoplastic diseases, such as HIV-associated lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, nasal NK/T lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and lymphoepithelial carcinoma.
- Guide treatment and prognosis:
1)EBV infectious diseases: Antiviral treatment, good prognosis
2)Lymphoproliferative diseases after organ transplantation: Better early prognosis
3)EBV-positive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma has a worse prognosis than EBV-negative. EBV-positive Hodgkin’s lymphoma has better or no significant difference in prognosis than EBV-negative.
4) Nasal NK/T cell lymphoma has poor prognosis.
Related Product







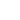 PRODUCT CATEGORY
PRODUCT CATEGORY





 Chat
Chat
 message
message

 Quote
Quote

 Download
Download